Public Credit Registry
What is the News?
 The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has shortlisted six major IT companies, including Tata Consultancy Services Ltd (TCS), Wipro Ltd and IBM India, to set up a wide-based digital Public Credit Registry for capturing details of all borrowers and wilful defaulters.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has shortlisted six major IT companies, including Tata Consultancy Services Ltd (TCS), Wipro Ltd and IBM India, to set up a wide-based digital Public Credit Registry for capturing details of all borrowers and wilful defaulters.
The proposed Public Credit Registry will also include data from entities like capital markets regulator Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), the corporate affairs ministry, Goods and Service Tax Network (GSTN) and the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI) to enable banks and financial institutions to get a 360-degree profile of the existing as well as prospective borrowers on a real-time basis.
What is Public Credit Registry?
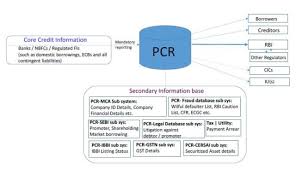 It is a digital registry of authenticated granular credit information and will work as a financial information infrastructure providing access to various stakeholders and enrich the existing credit information ecosystem.
It is a digital registry of authenticated granular credit information and will work as a financial information infrastructure providing access to various stakeholders and enrich the existing credit information ecosystem.- It will be an extensive database of credit information for India that is accessible to all stakeholders.
- It would be mandatory for reporting for all material events for each loan, notwithstanding any threshold in the loan amount or type of borrower to the Public Credit Registry.
- It will also allow borrowers to access their own credit information and seek corrections to the credit information reported on them.
Firms Shortlisted by RBI
- The firms shortlisted by the RBI are,
- TCS, Wipro, IBM India
- Capgemini Technology Services India
- Dun & Bradstreet Information Services India
- Mindtree Ltd.
Need of PCR
- There are multiple granular credit information repositories in India, with each having somewhat distinct objectives and coverage.
- Lack of integrated comprehensive information had become a bottleneck in tackling bad loans, Public credit registry will fill this gap.
- A central repository, captures and certifies the details of collaterals, can enable the writing of contracts that prevent over-pledging of collateral by a borrower.
- In absence of the repository, the lender may not trust its first right on the collateral and either charge a high cost on the loan or ask for more collateral than necessary to prevent being diluted by other lenders.
By: Eswar Sai

 The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has shortlisted six major IT companies, including Tata Consultancy Services Ltd (TCS), Wipro Ltd and IBM India, to set up a wide-based digital Public Credit Registry for capturing details of all borrowers and wilful defaulters.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has shortlisted six major IT companies, including Tata Consultancy Services Ltd (TCS), Wipro Ltd and IBM India, to set up a wide-based digital Public Credit Registry for capturing details of all borrowers and wilful defaulters. It is a digital registry of authenticated granular credit information and will work as a financial information infrastructure providing access to various stakeholders and enrich the existing credit information ecosystem.
It is a digital registry of authenticated granular credit information and will work as a financial information infrastructure providing access to various stakeholders and enrich the existing credit information ecosystem.