Industry, Trades and Commerce Schemes
SCHEMES COVERED
1. Start Up India Scheme
2. e-Biz
3. Niryat Bandhu Scheme
4. Merchandise Exports from India Scheme (MEIS)
5. Vishesh Krishi And Gram Udyog Yojana (VKGUY) (Special agriculture and village industry scheme)
6. Focus Market Scheme
7. Revenue Insurance Scheme for Plantation Crops (RISPC)
8. Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of (hybrid &) Electric vehicles (FAME) in India Scheme
9. A Scheme for Promotion of Innovation, Rural Industry & Entrepreneur-ship (ASPIRE)
10. Scheme of Fund for Regeneration of Traditional Industries (SFURTI)
11. Prime Minister’s Employment Generation Programme (PMEGP)
1. Start Up India Scheme
By : Ministry of Commerce and Industry
Objectives and Key Features :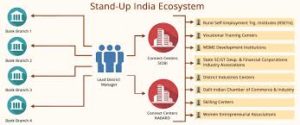
- Startup India campaign is based on an action plan aimed at promoting bank financing for startup ventures
- to boost entrepreneurship and encourage start-ups with jobs creation.
- Thus, it aims to build a strong eco-system for nurturing innovation and startups in the country which will drive economic growth and generate large scale employment opportunities.
- A startup is an entity that is headquartered in India which was opened less than seven years ago and has an annual turnover less than 25 crores.
2. e-Biz
By : Ministry of Commerce and Industry
What? : eBiz is one of the integrated services projects and part of the 31 Mission Mode Projects (MMPs) under the National E-Governance Plan (NEGP) of the GoI.
Objectives :
It aims at creating an investor-friendly business environment in India by making all regulatory information starting from the establishment of a business, through its ongoing operations, and even its possible closure – easily available to the various stakeholders concerned.
3. Niryat Bandhu Scheme
By : Ministry of Commerce and Industry
Objective :
To reach out to the new and potential exporters and mentor them through orientation programmes, counselling sessions, individual facilitation, etc., for being able to get into international trade and boost exports from India.
4. Merchandise Exports from India Scheme (MEIS)
By : Ministry of Commerce and Industry
What? : MEIS under Foreign Trade Policy of India (FTP 2015-20) is one of the 2 schemes introduced in Foreign Trade Policy of India 2015-20, as a part of Exports from India Scheme. (The other scheme is Service Exports from India Scheme-SEIS).
Objectives and Key Features :
- The objective of the scheme is to offset infrastructural inefficiencies and the associated costs of exporting products produced in India giving special emphasis on those which are of India’s ex-port interest and have the capability to generate employment and enhance India’s competitiveness in the world market.
- With the aim in making India’s products more competitive in the global markets, the scheme provides incentive in the form of duty credit scrip to the exporter to compensate for his loss on payment of duties. The incentive is paid as percentage of the realised FOB value (in free foreign exchange) for notified goods going to notified markets.
5. Vishesh Krishi And Gram Udyog Yojana (VKGUY) (Special agriculture and village industry scheme)
By : Ministry of Commerce and Industry
Objectives and Key Features :
To compensate high transport costs and offset other disadvantages to promote exports of the following products:
a. Agricultural Produce and their value added products;
b. Minor Forest Produce and their value added variants;
c. Gram Udyog Products;
d. Forest Based Products; and
e. Other Products, as notified from time to time.
6. Focus Market Scheme
By : Ministry of Commerce and Industry
Objectives and Key Features :
- The objective of FMS is to offset high freight cost and other externalities to select international markets with a view to enhance India’s export competitiveness in these markets.
- The exporters who export to notified FMS countries get Duty Credit Scrip equivalent to 3 % of FOB value of exports (in free foreign exchange) for exports.
- This scheme is only for Goods exports and not for Services. It also does not cover exports to SEZ, export of Precious, semiprecious stones, precious metals, jewellery, Ores, Minerals, Cereals and Sugar, Petroleum Products and Milk and Milk Products.
7. Revenue Insurance Scheme for Plantation Crops (RISPC)
By : Ministry of Commerce and Industry
Objectives and Key Features :
- This scheme is for protecting growers of tea, coffee, rubber, cardamom and tobacco from the twin risks of weather and price arising from yield loss due to adverse weather parameters, pest attacks etc. and from income loss caused by fall in international/domestic prices through crop insurance mechanism.
- The Scheme is to be implemented on pilot basis in eight districts in the States of West Bengal, Kerala, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Assam, Sikkim and Tamil Nadu by the Commodity Boards through selected insurance companies.
- The Price Stabilisation Fund (PSF) Scheme, 2003 was closed on September 30, 2013 and Revenue Insurance Scheme for Plantation Crops (RISPC) is an improved form of the PSF.
8. Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of (hybrid &) Electric vehicles (FAME) in India Scheme
By : Ministry of Heavy Industries and Public Enterprises
Objective :
- To support the hybrid/electric vehicles market development and its manufacturing eco-system.
- To be implemented till 2020 (from its launch it is a period of 6 years).
- To achieve self-sustenance at the end of the stipulated period.
9. A Scheme for Promotion of Innovation, Rural Industry & Entrepreneur-ship (ASPIRE)
By : Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME)
Objectives and Key Features :
- To promote start-ups for innovation and entrepreneurship in agro-industry.
- Under ASPIRE, 80 Livelihood Business Incubation (LBI) centres are to be set up in which a total of 104000 incubates will be trained and 30 (10 new & 20 existing) Technology Business Incubation (TBI) centres.
10. Scheme of Fund for Regeneration of Traditional Industries (SFURTI)
By : Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME)
Objective :
To organise the traditional industries and artisans into clusters to make them competitive and provide support for their long term sustainability, sustained employment.
Key Features :
- To enhance marketability of products of such clusters,
- To equip traditional artisans of the associated clusters with the improved skills,
- To make provision for common facilities and improved tools and equipments for artisans,
- To strengthen the cluster governance systems with the active participation of the stakeholders, and to build up innovated and traditional skills, improved technologies, advanced processes, market intelligence and new models of public-private partnerships, so as to gradually replicate similar models of cluster-based regenerated traditional industries.
- The financial assistance provided for any specific project shall be subject to a maximum of Rs 8 (eight) crore to support Soft, Hard and Thematic interventions.
11. Prime Minister’s Employment Generation Programme (PMEGP)
By : Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME)
What? :
- PMEGP has been launched by merging the two schemes that were in operation till 31.03.2008, namely Prime Minister’s Rojgar Yojana (PMRY) and Rural Employment Generation Programme (REGP) for generation of employment opportunities through establishment of micro enterprises in rural as well as urban areas.
- At the national level, the Scheme is being implemented by Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC), a statutory organisation under the administrative control of the Ministry of MSME as the single nodal agency.
- At the State level, the Scheme will be implemented through State KVIC Directorates, State Kha-di and Village Industries Boards (KVIBs) and District Industries Centres (DICs) and banks.

